Analogues
Analogues are copies of a project and can be used for purposes such as modeling of acquisition analogues, or planning based on typical wells. Consider shale gas as an example. Shale gas wells have a few key characteristics:
- The wells decline rapidly, so there is a constant need to drill more wells to maintain production.
- The production from the wells is very consistent: all of them produce a very similar profile.
- For a fully-developed shale gas field you need to drill hundreds or even thousands of wells.
In this case, you can set up different scenarios (probably four or five) to model the typical shale gas well profiles. Then you can apply constraints saying how many wells you can drill in a year in each field (based on rig availability and other factors). You can also have other typical targets such as production, maximum capital, and so on.
Analogues are displayed in the Projects View. To view them, right-click on a column, select Column Chooser and drag the Analogue band into the table. Columns included into the Analogue band are described in the table below.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Is Analogue? | Indicates whether the selected project contains any analogues. |
| # of Steps | Number of analogues in the selected project. |
| Step Size | Intervals between analogue start dates (in months). |
| Min Total | Minimum number of analogues that the selected project can contain. |
| Max Total | Maximum number of analogues that the selected project can contain. |
To add analogues:
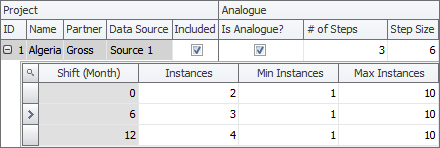
- Check the Is Analogue? box and a table will be displayed under the project as shown below.
- Specify the number of analogues in the # of Steps field. For each analogue, a row will be added to the table. The image below shows three rows which means that the project consists of three analogues.
- The Shift (Month) column is filled in automatically depending on the step size. In the image above, the step size is 6 which means that the second analogue will start 6 months after the first one, the third analogue will start 12 months after the first one, and so on.
- Specify the number of instances in each analogue. Each instance contains a copy of all project data; for example, having two instances is the same as doubling all variable values.
- You can limit the number of instances in each step by entering values in the Min Instances and Max Instances fields. These limits are used, for example, if several regions are geographically adjacent and can therefore share rigs. The minimum is important if you have to keep a minimum activity level to keep your license. The Min Instances and Max Instances fields are also used as limits for optimizations.
On charts, projects are displayed in the same way whether they contain analogues or not.
